A trail camera won’t stumble through a bedding area, leave scent all over a trail, or exaggerate the size of a rack. And it’ll never oversleep. But your perfect little scouting buddy must be chosen wisely and placed carefully if you want to pattern that old, crafty animal you know is around. Here’s how…
The earlier version trail cameras were just a 35mm film point-and-shoot tucked in a weatherproof housing. It snapped a single picture when something triggered the sensor. After retrieving the camera, you ran to the one-hour shop to get the film developed, then thumbed through a week’s worth of pictures. More than once a stack of 36 prints revealed a handful of out-of-focus animals and a couple dozen shots of a wind-whipped brush or a drooping tree branch. That was only a few years ago.
Today, many website boasts several pages of trail cams, and even the cheapest one outperforms the original older ones. They have lenses sharp enough to count the ticks on a deer’s neck, electronic circuit boards so efficient that four AA batteries will run a unit for months, and memory cards that hold thousands of pictures you can download to your computer or delete at the touch of a button. And those are standard features on mid-priced cameras. The high-end ones will send a photo to your cellphone or laptop.
Like everything in the digital age, trail-cam technology has improved, competition has become fierce, and prices have plunged. Still, $200 is plenty of money, and matching a camera with the right features to meet your needs is critical. And even the best camera can’t take spectacular photos of a trophy buck if you don’t set it properly. But it’s not difficult to get started. These are the basics.
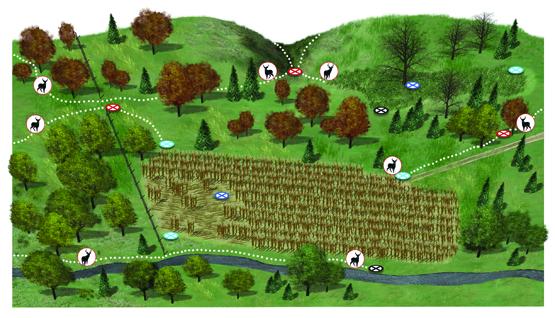
Wildlife biologists use trail cams to measure herd densities, buck-to-doe ratios, and the like. Your goals should be simpler: learning about the deer on your property, figuring out where to hunt them, and having fun in the process. You can pinpoint ideal spots before you buy a camera, and the locations you choose can determine what model is best for you. Here are four sites for four different periods.
Time: Late Summer
Site: Mineral lick
Goal: To start an inventory of buck numbers and quality on your property.
Setup: Find a spot with moderate to heavy deer traffic and spade up dirt in a 2-foot circle. Pour in half of an ice-cream pail of stock salt or commercial deer mineral and spade it into the loosened soil. Pour the rest on top.
Tips:
• Establish one or two licks per 80 acres. Allow deer up to a week to find them.
• Situate each lick 10 to 30 feet from a tree for mounting a camera.
• Jam a stick behind the camera’s top edge to point it down toward the lick.
 Time: Early Season
Time: Early Season
Site: Mock scrape
Goal: To find bucks after velvet shed, when they often relocate. Mocks can draw up to 90 percent of the bucks you’ll hunt.
Setup: Rake grass and forest debris 5 feet away from a tree that has a green, overhanging licking branch 5 to 7 feet above the ground. Activate with your own “product” (drink plenty of liquids) or deer urine.
Tips:
• If you are not getting clear shots of a buck, aim the camera at the licking branch. Most bucks will work it with their antlers.
• Establish multiple scrapes in each area and hang cameras only on the most active ones.
Time: Rut
Site: Funnel
Goal: To determine where resident bucks are traveling and whether traveling bucks are in the area.
Setup: Find terrain features that channel buck movement and hang a camera near fresh tracks and rubbing activity. Check camera every three to five days—the rut moves quickly.
Tips:
• Mount camera at a 45-degree angle to the trail. Bucks often move through funnels quickly; a camera set perpendicular to the trail might miss the shot.
• Scuff dirt in front of the camera with a boot. Such a mini mock will often make a moving buck pause and get “shot.”
Time: Late Season
Site: Food source
Goal: To find out where to fill a last-minute tag, and to know which bucks have survived the bulk of the hunting season.
Setup: Scout widely to find the hot food sources in your area, such as waste grainfields and clear-cuts. Place camera within 30 feet of the most heavily trafficked area. Load it with fresh batteries if you hunt in an extremely cold area.
Tips:
• Set up and check cameras at midday to avoid spooking feeding deer.
• If no trees are located near the food source, mount the camera on a tripod and camouflage it with grass or brush.
Make the Next Shot Count!
Follow our FISHING BLOG
WEB RATES FISH HUNT CABINS PHOTOS T
ESTIMONIALS BROCHURE HUNT BOOKLET





















