
You know what a buck rub looks like. You know that bigger bucks tend to rub bigger trees, and you’re probably aware that a buck travels in the direction facing the rubbed side of a tree. But there’s more to be gleaned from a savaged sapling. The right rub can tell you the size of a buck’s rack, whether he has any beauty points, and how to hunt him.
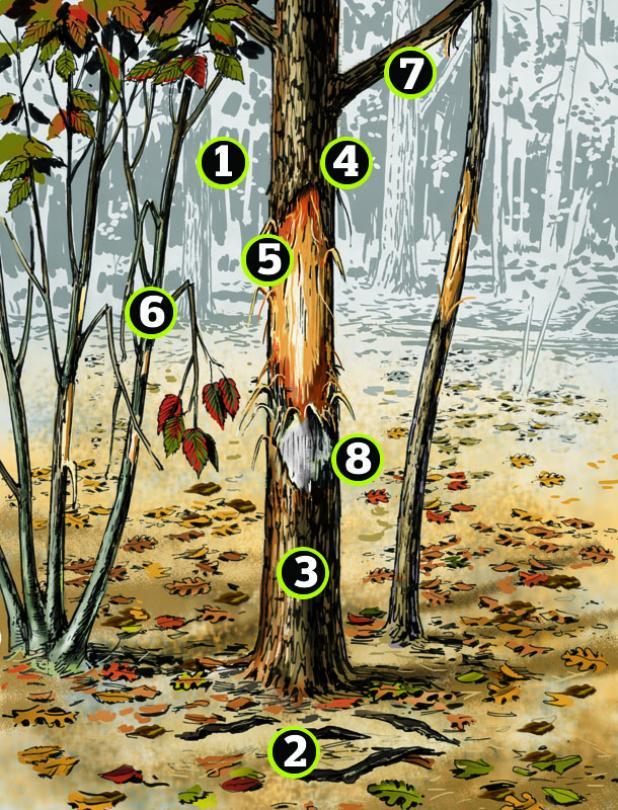
1. Time of Day
In hilly country, buck rubs that are visible when facing uphill were likely made in the morning as the buck traveled back to his high-ground bedding area. Likewise, the ones you see when looking downhill were probably made in the evening. Wherever feeding areas are open and obvious, such as crop fields, rubs that show when you’re facing into the woods are morning rubs. Their opposites are evening rubs.
2. Velvet Proof
Where there’s off-track ATV travel, it can be difficult to distinguish between a tree that’s been debarked by a buck and one that’s been scraped by a four-wheeler. During preseason and early-season scouting, look for shed velvet on the ground beneath the rub. You won’t always find it—velvet dries quickly and bucks sometimes eat it—but it’s a sure sign when it’s there.
3. Big Tree, Big Buck
This familiar rule of thumb is valid. But remember, there are plenty of exceptions. A mature buck with a narrow tip-to-tip spread or other unusual rack configuration may not be able to rub a large-diameter tree in the usual way.
4. High Rub, Big Buck
Though far less familiar, this is a good rule of thumb, too. A mature buck is taller and stronger and therefore tends to rub higher off the ground. Caveat: This only applies to fresh rubs in fall. Snowpack can affect rub height, giving you a false reading late in the season.
5. Non-typical Marks
Sticker points, split brow tines, and other odd pieces of bone commonly leave corresponding deep, off-center gouges on the tree trunk, branches, or adjacent trees, which can help you identify a specific buck.
6. Rack Width
Wherever you find rubs on multi trunked or closely clumped trees, look for scars or broken branches on saplings and shrubs adjacent to the main rub. They can tell you how wide a buck’s rack is.
7. Tine Length
Look on the underside of branches, too. A tall-tined buck may leave nicks or scraped bark on branches a foot or more above the main rub.
8. Color Clues
Keep an eye peeled for old rubs. A mixture of light-colored new rubs, gray weathered rubs, and often blackish healing-over rubs reveals a perennial favorite buck route and also suggests that the animal making them is now mature.
Follow our FISHING BLOG
WEB RATES FISH HUNT CABINS PHOTOS
TESTIMONIALS BROCHURE HUNT BOOKLET















